A data source represents an authorized connection to any third-party service from where data is extracted. Through a data flow, you send data from your data source to a data destination on a regular basis, based on the schedule you configured during the data source setup.
You can create a data source by connecting to a variety of services including:
- SaaS apps (e.g. Salesforce, NetSuite, HubSpot, Stripe, Klaviyo, Facebook Ads, Google Analytics 4)
- Databases (e.g. MySQL, Postgres, SQL Server)
- Cloud data warehouses (e.g. BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, Snowflake)
- File storages (e.g. Amazon S3, SFTP)
Creating a Data Source
Starting a data source begins with choosing a connector that shapes the initial setup.
Dataddo provides three kinds of connectors, catering to various requirements:
- Universal connectors: These allow highly customizable, low-level interactions with various systems. Examples include JSON, XML, CSV, and database options like MySQL and Postgres.
- Fixed-schema connectors: These offer pre-defined schemas (datasets) making them easy to set up but they are also are less flexible. Examples include Mailchimp, ExactOnline, and Google Search Console.
- Custom-schema connectors: These allow dynamic schema definitions tailored to services with custom attributes. Examples include Hubspot, Google Analytics 4, Salesforce, and Facebook Ads.
For more details, check out our article on types of connectors.
Source Detail
On the Sources page, click on your data source to see your Source Details.
On the Basic Info tab:
- Change your data source name and add a description for internal purposes
- Find your source ID for error reporting purposes
- Enable the Allow Empty option if you are expecting days without data (for more information, see No Data Retrieved Error Message)
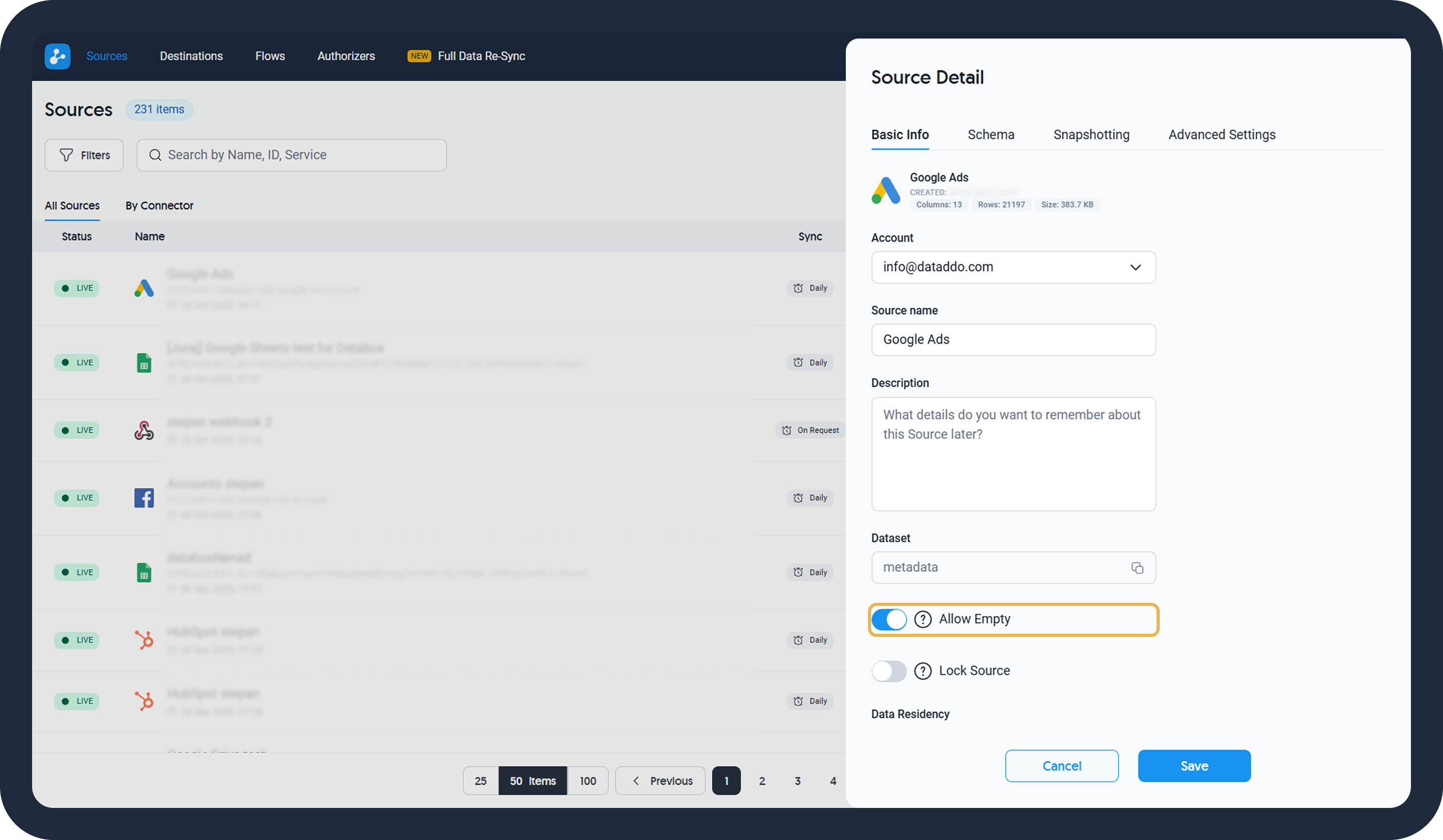
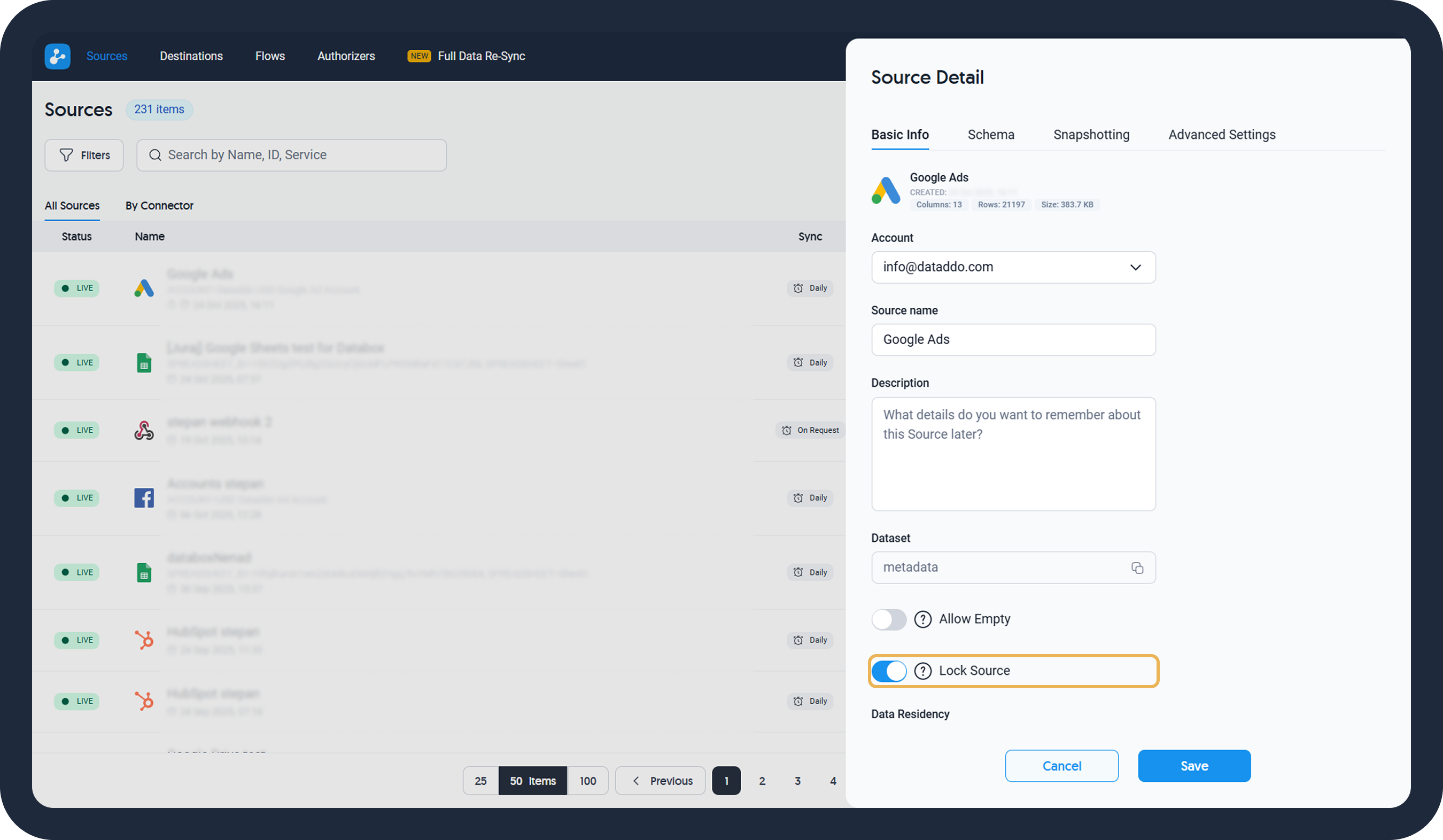
- Lock the source to prevent it from modifications
On the Schema tab:
- Edit your source schema by changing data types or data labels (= column names)
On the Snapshotting tab:
On the Advanced Settings tab:
- Edit data source URL for e.g. setting date range or data backfilling
Other Data Source Operations
Duplicate/Clone a Data Source
Duplicating or cloning a data source is useful, for example when
- You need to change your data source schema but want to ensure data consistency and avoid unintended disruptions in downstream systems, like your data warehouse.
- You need versioning for your data source. By cloning the existing source, you can make modifications to its parameters without affecting the original setup. This allows you to maintain various versions of a source configuration to meet different needs.
Simply click on the Clone Settings button next to your source and proceed with the on-screen prompts.
Delete a Source
To delete a data source and its associated flows:
- Go to the Sources page.
- Click the bin icon for the relevant data source.
- In the confirmation window, view the connected flows that will also be removed.
- Type DELETE to confirm your decision.
Broken Source Operations
Restart a Source
If a data source enters a broken state, you can attempt to restart it. If successful, the source becomes live again, allowing manual data loading. If restarting fails, troubleshooting options will be available.
Extraction Logs
To ensure a transparent view of the entire extraction process, each data source maintains logs of all extraction attempts. To access these logs:
- Click on the three-dots icon next to the relevant data source and choose Show Logs (available for live sources as well).
- Alternatively, click on the Show Logs icon directly.
For help with resolving issues, refer to the troubleshooting guide.
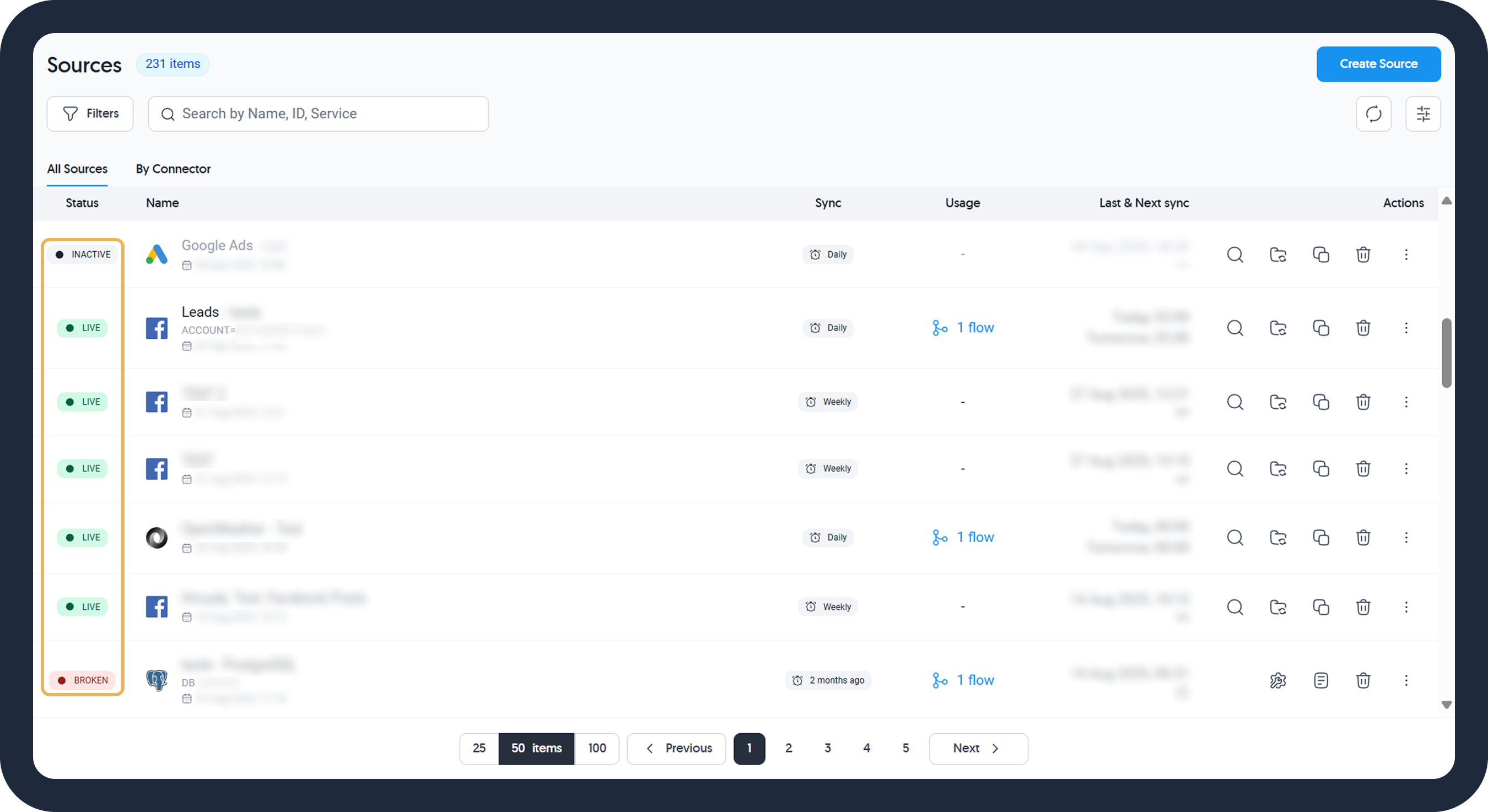
Source Status
A data source will have one of the following statuses.
| Source Status (Color) | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Live (Green) | Indicates normal operation; data is being successfully extracted. |
| Reconnecting (Orange) | Shown after a failed extraction attempt; the system will try to reconnect and extract data up to three times before changing to Broken. |
| Broken (Red) | Signifies that all attempts to extract data have failed. Restarting is necessary to resume operations. Please see how to fix a broken source. |
| Inactive (Gray) | The source is not in use. Manually restart to return it to Live status. |
Related Articles
Troubleshooting
Error Reporting Best Practice
Troubleshooting
Extraction Logs
Other Resources
Data Duplication
Data Sampling